In today's fast-paced industrial landscape, maintaining machinery and equipment at optimal performance levels is paramount for sustained productivity and profitability. To meet this demand, businesses turn to innovative solutions like SAP PM (Plant Maintenance). In this article, we'll delve into the essence of SAP PM, explore its organizational structure, elucidate its pivotal role in modern enterprises, and unravel the myriad benefits it offers.
Understanding SAP PM:
SAP PM, part of the SAP ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) suite, is a robust solution designed to streamline and automate the maintenance of assets within an organization. It encompasses a range of functionalities tailored to manage all aspects of plant maintenance, from routine inspections to complex repairs. At its core, SAP PM facilitates the efficient planning, execution, and monitoring of maintenance tasks, ensuring optimal asset performance and uptime.
Uses and Benefits of SAP PM:
Streamlined Maintenance Processes: SAP PM centralizes maintenance activities, enabling organizations to create structured maintenance plans, schedule tasks, and track work orders seamlessly. This streamlined approach enhances operational efficiency by reducing downtime and optimizing resource utilization.
Predictive Maintenance: Leveraging advanced analytics and IoT (Internet of Things) integration, SAP PM empowers predictive maintenance strategies. By analyzing equipment data in real-time, organizations can anticipate potential failures, preemptively address issues, and avoid costly unplanned downtime.
Enhanced Asset Visibility: With SAP PM, businesses gain comprehensive visibility into their asset portfolio. Detailed asset records, including maintenance history, performance metrics, and associated documentation, provide valuable insights for informed decision-making and resource allocation.
Compliance and Safety: By enforcing standardized maintenance procedures and regulatory compliance requirements, SAP PM helps mitigate risks and ensure workplace safety. From equipment inspections to regulatory reporting, organizations can uphold industry standards with confidence.
Optimized Inventory Management: Efficient inventory management is integral to maintenance operations. SAP PM facilitates proactive spare parts management, enabling organizations to optimize inventory levels, minimize stockouts, and streamline procurement processes.
Cost Control and Budgeting: Effective cost control is essential for maintaining profitability. SAP PM offers robust budgeting and cost-tracking features, allowing organizations to monitor maintenance expenditures, analyze cost trends, and optimize spending for maximum ROI.
Seamless Integration: As part of the SAP ecosystem, SAP PM seamlessly integrates with other SAP modules, such as SAP MM (Materials Management) and SAP FI (Financial Accounting), fostering data consistency and process efficiency across the enterprise.
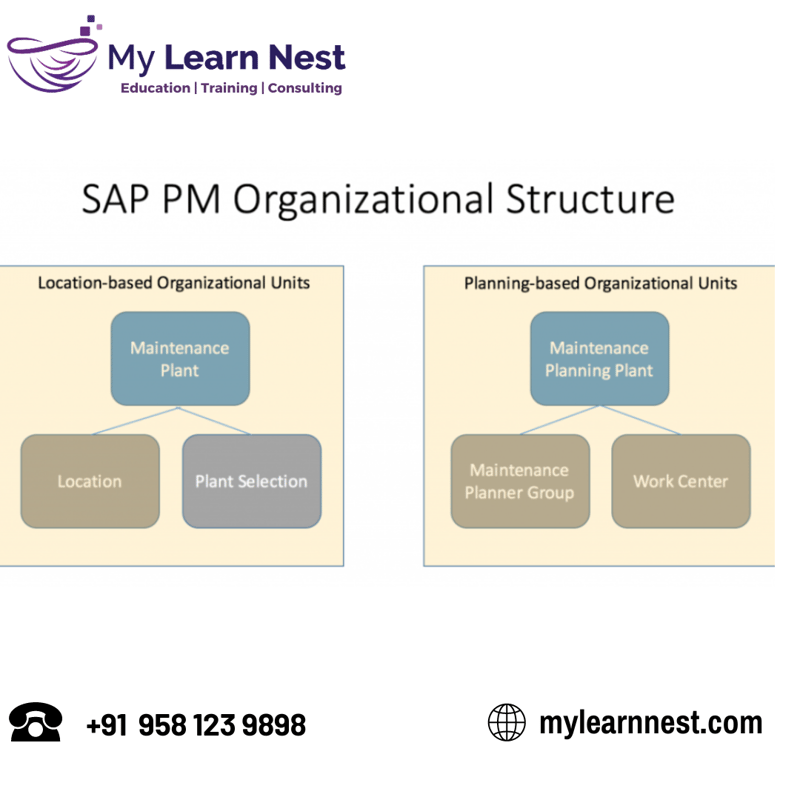
SAP PM Organizational Structure:
The organizational structure within SAP PM is designed to reflect the hierarchical arrangement of maintenance resources and activities within an organization. At its core, the SAP PM organizational structure comprises the following key elements:
Maintenance Plant: The highest level in the hierarchy, the maintenance plant represents a physical or logical grouping of maintenance resources, such as equipment, machinery, or production units. Each maintenance plant is assigned specific organizational attributes and serves as a basis for maintenance planning and execution.
Maintenance Work Center: Work centers within SAP PM represent physical locations where maintenance activities take place. They serve as operational units responsible for executing maintenance tasks, such as inspections, repairs, and preventive maintenance. Work centers can be associated with specific functional areas or departments within the organization.
Functional Location: Functional locations denote specific equipment or assets within a maintenance plant. They provide a structured framework for organizing maintenance objects and capturing relevant information, such as equipment hierarchy, technical specifications, and maintenance history. Functional locations serve as reference points for maintenance planning and execution.
Equipment: Equipment objects represent individual assets or components within a functional location. They encompass tangible items, such as machinery, tools, or vehicles, requiring maintenance activities. Each equipment object is assigned unique identifiers and attributes, facilitating precise tracking and management throughout its lifecycle.
Role of SAP PM:
The role of SAP PM extends far beyond traditional maintenance management. As a cornerstone of enterprise asset management (EAM), SAP PM plays a multifaceted role in driving operational excellence, fostering innovation, and enabling strategic decision-making. Some key aspects of SAP PM's role include:
Facilitating Collaboration: SAP PM serves as a collaborative platform, enabling cross-functional teams to coordinate maintenance activities, share knowledge, and collaborate in real-time. By fostering communication and collaboration, SAP PM enhances organizational agility and responsiveness to maintenance challenges.
Empowering Data-Driven Insights: With its robust analytics capabilities, SAP PM transforms raw data into actionable insights, empowering organizations to make informed decisions and optimize maintenance strategies. By leveraging predictive analytics, organizations can anticipate equipment failures, prioritize maintenance tasks, and optimize resource allocation for maximum efficiency.
Driving Continuous Improvement: SAP PM facilitates a culture of continuous improvement by providing tools and frameworks for performance monitoring, benchmarking, and process optimization. Through key performance indicators (KPIs) and performance dashboards, organizations can identify areas for improvement, implement corrective actions, and drive operational excellence across the maintenance lifecycle.
Supporting Regulatory Compliance: In highly regulated industries, compliance with safety, environmental, and quality standards is paramount. SAP PM helps organizations adhere to regulatory requirements by enforcing standardized processes, maintaining audit trails, and generating compliance reports. By ensuring regulatory compliance, SAP PM helps mitigate risks and safeguard organizational reputation.
Enabling Asset Lifecycle Management: From asset acquisition to disposal, SAP PM enables organizations to manage the entire lifecycle of their assets efficiently. By integrating maintenance activities with asset lifecycle management processes, organizations can optimize asset performance, extend asset lifespan, and maximize return on investment (ROI).
conclusion:
SAP PM stands as a cornerstone of modern maintenance management, empowering organizations to unlock efficiency, ensure asset reliability, and drive operational excellence. By streamlining maintenance processes, enhancing asset visibility, and fostering collaboration, SAP PM enables organizations to stay ahead in today's competitive landscape. Embracing SAP PM is not just a technological investment but a strategic imperative for organizations striving to thrive in an increasingly complex and dynamic business environment.