Given the array nums consisting of 2n elements in the form [x1,x2,...,xn,y1,y2,...,yn].
Return the array in the form [x1,y1,x2,y2,...,xn,yn].
Example -
Input: nums = [2,5,1,3,4,7], n = 3
Output: [2,3,5,4,1,7]
Explanation: Since x1=2, x2=5, x3=1, y1=3, y2=4, y3=7
then the answer is [2,3,5,4,1,7].
In this technique we try to store two numbers at one Index by multiplying the number with 10000;
As we know our Constraints number can be up to 1000 so we are multiplying it with 10000, so that if the numbers are of 4 digits we can store all of them.
This multiplying number can be increased as per our input number size increases.
⚠ I'm using pointers for easy explanation but we can do it without them.
Explanation
Step 1.
In first loop we store two numbers at one index.
// let's say Our input is [1,2,3,4,5,6]
We will run our first loop from 0 to n / 2 - 1 and n / 2 to n - 1; So basically first pointer will run for [1,2,3] and second pointer will run for [4,5,6].
And we will keep multiplying the rightPointer to 10000 and add our leftPointer to result and store it at leftPointer position.
let leftPointer = 0;
let rightPointer = nums.length / 2;
while(leftPointer < nums.length / 2 && rightPointer < nums.length){
nums[leftPointer] = nums[rightPointer]+(nums[leftPointer] * 10000);
leftPointer++;
rightPointer++;
}
Now my result array becomes - [10004, 20005, 30006, 4, 5, 6];
Step 2.
Now In our second loop we divide and mod the converted number and place the result at respective place.
This time we will start our indexes in reverse order.
- LeftPointer will start from
nums.length / 2 - 1and go to0; We decrease it by 1 each time. - RightPointer will start from
nums.length - 1. We will decrease it by 2 each time because we store 2 items at end.
So in first loop our rightPointer will point to [6] and our leftPointer will point to 3006.
And when we divide and mode [30006] by 10000 we get 3 and 6
now store these 3 and 6 at the end of the nums[].
And we keep doing it until we reaches 0th position of array.
See the below loop, we initialized left and right pointers respectively and looping over the big numbers which we created in earlier loop. Now we get the resultant two numbers and store them at the rightPointer.
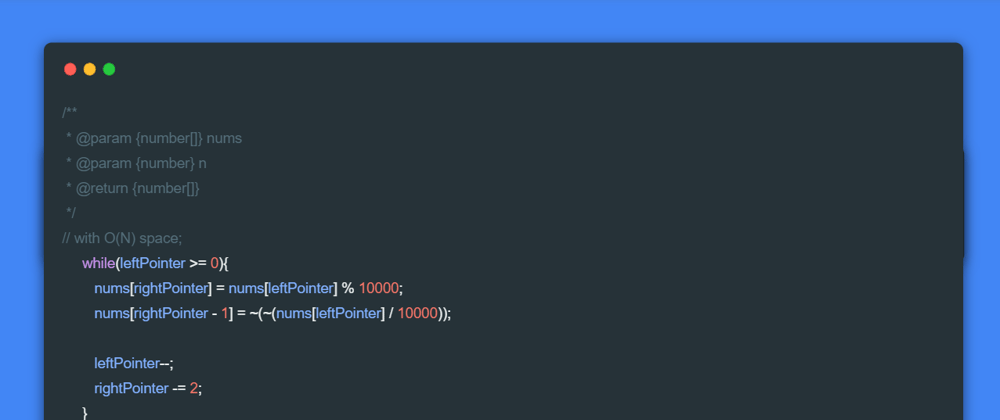
leftPointer = nums.length / 2 - 1
rightPointer = nums.length - 1;
while(leftPointer >= 0){
nums[rightPointer] = nums[leftPointer] % 10000;
nums[rightPointer - 1] = ~(~(nums[leftPointer] / 10000));
leftPointer--;
rightPointer -= 2;
}
Source code.
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @param {number} n
* @return {number[]}
*/
var shuffle = function(nums, n){
let leftPointer = 0;
let rightPointer = nums.length / 2;
while(leftPointer < nums.length / 2 && rightPointer < nums.length){
nums[leftPointer] = nums[rightPointer]+(nums[leftPointer] * 10000);
leftPointer++;
rightPointer++;
}
leftPointer = nums.length / 2 - 1
rightPointer = nums.length - 1;
while(leftPointer >= 0){
nums[rightPointer] = nums[leftPointer] % 10000;
nums[rightPointer - 1] = ~(~(nums[leftPointer] / 10000));
leftPointer--;
rightPointer -= 2;
}
return nums;
}