Hi there! I am writing a series of articles called "Web Performance Hacks" and this will be the first article from the series.
This article aims to show how browsers parse and render HTML and CSS which will eventually help us in understanding how we can trick the browser's parser to improve web performance.
TLDR;
- Parsing and Rendering turn the HTML content into a web page with colors and backgrounds and pictures.
- HTML Parsing: HTML Text -> Tokenization -> DOM Tree
- CSS Parsing: CSS Text -> Tokenization -> CSSOM Tree
- DOM and CSSOM are merged to form a Render Tree
- Render Tree has all the information required to mark and paint the screen.
- Render Tree -> Layout -> Paint
- The layout does the maths for placing the elements
- Paint paints the elements with colors, backgrounds, shadows, etc.
SO LETS GOOO!!!!
First, let's see what happens when you type a URL and hit enter
How browsers work
We type a URL and press the enter and the server responds with index.html. However, an HTML content is not what we see when we visit a website... we see a web page with colors and backgrounds and animations and pictures. So there's a process that turns the HTML content to a pretty webpage, and that is parsing and rendering!

Note: This is a zoomed-out view and there are other things like DNS resolving and other networking side of things that I've ignored to simplify the article
HTML Parsing
So we have HTML content at the beginning which goes through a process called tokenization, tokenization is a common process in almost every programming language where code is split into several tokens which are easier to understand while parsing. This is where the HTML's parser understands which is the start and which is the end of the tag, which tag it is and what is inside the tag.
Now we know, html tag starts at the top and then the head tag starts before the html ends so we can figure out that the head is inside html and create a tree out of it. Thus we then get something called a parse tree which eventually becomes a DOM tree as shown in the image below:

DOM tree is what we access when we do document.getElementById or document.querySelector in JavaScript.
Just like HTML, CSS goes through a similar process where we have the CSS text and then the tokenization of CSS to eventually create something called a CSSOM or CSS Object Model.
This is what a CSS Object Model looks like:

Awesome! now we have DOM and CSSOM so we got every information that is required to get our screens painted!
Rendering of Web Page
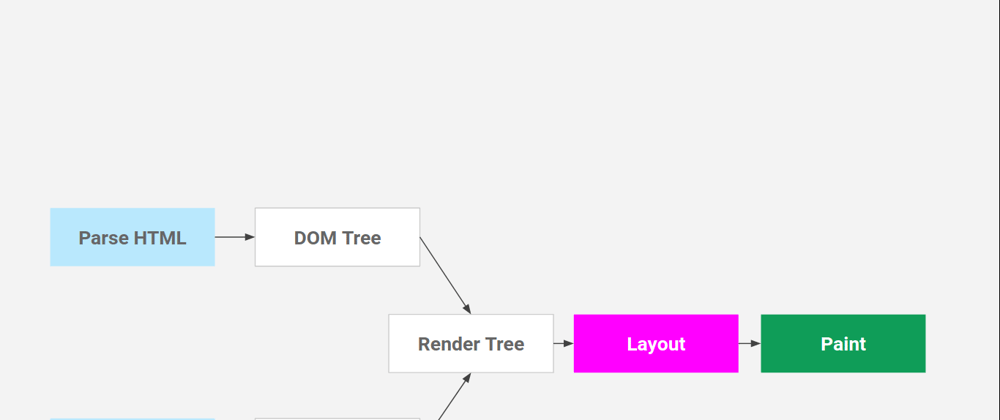
For rendering, a DOM and CSSOM are merged to form something called a Render Tree. Render Tree has the information required to mark and paint elements on the screen.

Also while forming a Render Tree, elements like <head>, <link>, <script>, and elements with 'display: none' in CSS are ignored since they are not rendered on the screen.
Note that the elements with 'opacity:0' or 'visibility: none' are included in the render tree, even though they are not painted on the screen they do take their positions and render as an empty space and thus are required for calculations.
Huushh! you've come a long way! drink a glass of water maybe?
So now we have a render tree with all the information that is needed to create a visual page. Now, the renderer will use this information to create a Layout and then a Paint, we will talk about Layout and Paint in next point before that here's what the overall process looks like:
Layout
The layout is where the elements are marked on the screen. The layout includes all the calculations and mathematics behind an element's position so it takes all the properties related to the position (height, width, position, top left right bottom, etc) from The Render Tree and places the elements on the screen.
Paint
After Layout, a Paint happens. Paint takes properties like color, background-color, border-color, box-shadow, etc. to paint the screen with colors.
After the paint, we see the content on the screen and the first time we see something other than a white screen is called 'First Paint'. The term First Paint is used in performance reports to show how long your website took to show something on the screen.
Gotchas!
Now, there are few important points to note in the whole process of parsing and rendering such as,
- Parsing halts when it comes across <link>, <script>, and <style> tag.
So if I have <script src="path/to/script"></script> in the middle of the HTML, The parser will halt there, will fetch the script, wait for the response, execute it and then it will continue the parsing. This is why we put <scipt> at the end of the body so that we can complete the parsing first.
A similar thing happens when we put <link rel="stylesheet" href="path/to/css" />. The parser fetches the CSS and makes sure that the CSSOM is ready before putting content on the screen. This is why we don't see a flash of CSSless content before the page load instead we see the content with its CSS loaded and applied.
Even though I said that the parsing halts when it comes across <link> and <script>, there are ways to avoid that using async and defer on the <script> tag and rel="preload" on <link> We'll see that in details in the next part of this series.
Anddd... we're done! Thank you for reading the article!!