In the previous post, I've created a Kubernetes Cluster on the Oracle Cloud. In this post I'll install YugabyteDB
Namespace
I'm creating a namespace to install YugabyteDB
dev@cloudshell:~ (uk-london-1)$
kubectl create namespace yb-demo
namespace/yb-demo created
Storage class
I'm changing the default StorageClass to oci-bv, the recommended Container Storage Interface (CSI) volume plugin, rather than the default oci (the FlexVolume one). I need this also to ensure that the block volume are in the same availability domain as the compute instance of the worker.
dev@cloudshell:~ (uk-london-1)$
kubectl patch storageclass oci \
-p '{"metadata": {"annotations":{"storageclass.beta.kubernetes.io/\
is-default-class":"false"}}}'
storageclass.storage.k8s.io/oci patched
dev@cloudshell:~ (uk-london-1)$
kubectl patch storageclass oci-bv \
-p '{"metadata": {"annotations":{"storageclass.kubernetes.io/\
is-default-class":"true"}}}'
storageclass.storage.k8s.io/oci-bv patched
Result:
dev@cloudshell:~ (uk-london-1)$
kubectl get sc
NAME PROVISIONER RECLAIMPOLICY VOLUMEBINDINGMODE ALLOWVOLUMEEXPANSION AGE
oci oracle.com/oci Delete Immediate false 1h
oci-bv (default) blockvolume.csi.oraclecloud.com Delete WaitForFirstConsumer true 1h
Helm chart
I'll install the latest version from the Helm Chart:
dev@cloudshell:~ (uk-london-1)$
helm repo add yugabytedb https://charts.yugabyte.com
"yugabytedb" already exists with the same configuration, skipping
dev@cloudshell:~ (uk-london-1)$
helm repo update
Hang tight while we grab the latest from your chart repositories...
...Successfully got an update from the "kubernetes-dashboard" chart repository
...Successfully got an update from the "yugabytedb" chart repository
Update Complete. ⎈Happy Helming!⎈
dev@cloudshell:~ (uk-london-1)$
helm search repo yugabytedb/yugabyte
NAME CHART VERSION APP VERSION DESCRIPTION
yugabytedb/yugabyte 2.13.0 2.13.0.0-b42 YugabyteDB is the high-performance distributed ...
YugabyteDB Configuration
I'll customize two things here from the values.yaml:
- The storage (I'll put 1 TeraByte for each PersistentVolumeClaim)
- The placement info (YugabyteDB must know on which Availability Domain it runs to ensure correct balancing of leaders and followers to be resilent to one AD failure).
The default is Replication Factor RF=3.
cat > yb-demo.yaml <<'YAML'
storage:
master:
size: 1Ti
tserver:
size: 1Ti
gflags:
master:
placement_cloud: $(curl -s http://169.254.169.254/opc/v1/instance/regionInfo/realmDomainComponent)
placement_region: $(curl -s http://169.254.169.254/opc/v1/instance/region)
placement_zone: $(curl -s http://169.254.169.254/opc/v1/instance/ociAdName)
tserver:
placement_cloud: $(curl -s http://169.254.169.254/opc/v1/instance/regionInfo/realmDomainComponent)
placement_region: $(curl -s http://169.254.169.254/opc/v1/instance/region)
placement_zone: $(curl -s http://169.254.169.254/opc/v1/instance/ociAdName)
YAML
Note that some screenshots later have been taked without this customization and show 50GB storage (the minimum in OKE) and cloud1/zone1/rack1 default placement. The right placement info is here: https://twitter.com/FranckPachot/status/1511976648807260162
YugabyteDB Install
The install takes a few minutes:
dev@cloudshell:~ (uk-london-1)$
helm install yb-demo yugabytedb/yugabyte --namespace yb-demo \
-f yb-demo.yaml --wait
NAME: yb-demo
LAST DEPLOYED: Wed Apr 6 08:40:02 2022
NAMESPACE: yb-demo
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
1. Get YugabyteDB Pods by running this command:
kubectl --namespace yb-demo get pods
2. Get list of YugabyteDB services that are running:
kubectl --namespace yb-demo get services
3. Get information about the load balancer services:
kubectl get svc --namespace yb-demo
4. Connect to one of the tablet server:
kubectl exec --namespace yb-demo -it yb-tserver-0 bash
5. Run YSQL shell from inside of a tablet server:
kubectl exec --namespace yb-demo -it yb-tserver-0 -- /home/yugabyte/bin/ysqlsh -h yb-tserver-0.yb-tservers.yb-demo
6. Cleanup YugabyteDB Pods
For helm 2:
helm delete yb-demo --purge
For helm 3:
helm delete yb-demo -n yb-demo
NOTE: You need to manually delete the persistent volume
kubectl delete pvc --namespace yb-demo -l app=yb-master
kubectl delete pvc --namespace yb-demo -l app=yb-tserver
Pods
Here are the pods created in my yb-demo namespace:
dev@cloudshell:~ (uk-london-1)$
kubectl get pods -n yb-demo -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
yb-master-0 2/2 Running 0 12m 10.244.0.4 10.0.10.51 <none> <none>
yb-master-1 2/2 Running 0 12m 10.244.1.3 10.0.10.152 <none> <none>
yb-master-2 2/2 Running 0 12m 10.244.0.131 10.0.10.103 <none> <none>
yb-tserver-0 2/2 Running 0 12m 10.244.0.132 10.0.10.103 <none> <none>
yb-tserver-1 2/2 Running 0 12m 10.244.1.4 10.0.10.152 <none> <none>
yb-tserver-2 2/2 Running 0 12m 10.244.0.5 10.0.10.51 <none> <none>
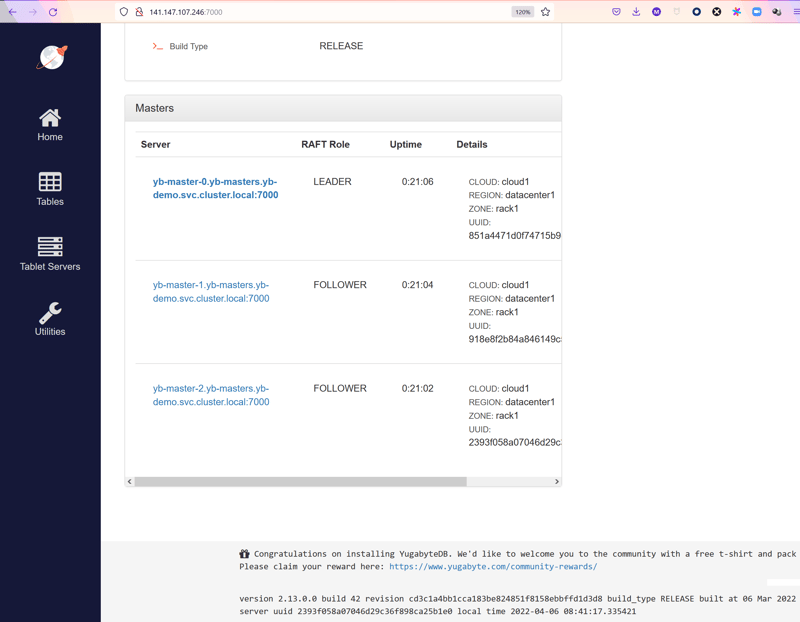
I have 3 master which are the control plane of the YugabyteDB cluster, and 3 tserver which are the data plane. 3 is the minimum because, for high availability, the cluster is in replication factor RF=3 (You can change that in the helm install with --set gflags.tserver.replication_factor=5 for example). This means 3 master where one is the leader and the two others are follower, ready to become leader in case of an Availability Domain outage. And at least 3 tserver for the same reason, be we can have more to distribute connections, load and data to many nodes.
Services
The master and tserver expose a web console, and the SQL endpoints, through a headless service ClusterIP that is accessible though a LoadBalancer:
dev@cloudshell:~ (uk-london-1)$
kubectl get services -n yb-demo -o wide
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE SELECTOR
yb-master-ui LoadBalancer 10.96.187.203 141.147.107.246 7000:31290/TCP 17m app=yb-master
yb-masters ClusterIP None <none> 7000/TCP,7100/TCP 17m app=yb-master
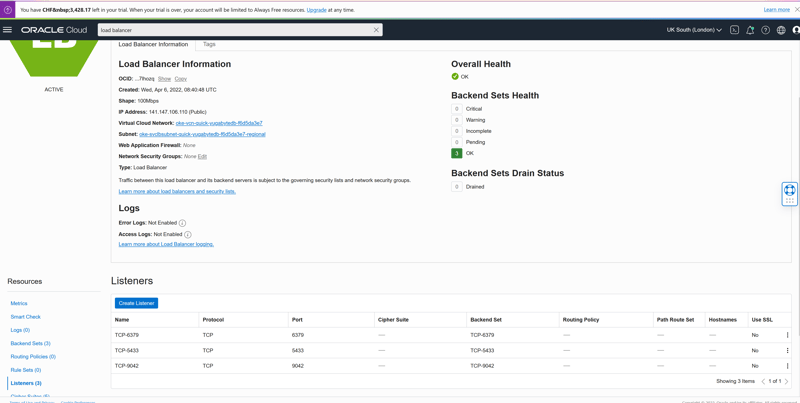
yb-tserver-service LoadBalancer 10.96.122.104 141.147.106.110 6379:32100/TCP,9042:30198/TCP,5433:31343/TCP 17m app=yb-tserver
yb-tservers ClusterIP None <none> 9000/TCP,12000/TCP,11000/TCP,13000/TCP,9100/TCP,6379/TCP,9042/TCP,5433/TCP 17m app=yb-tserver
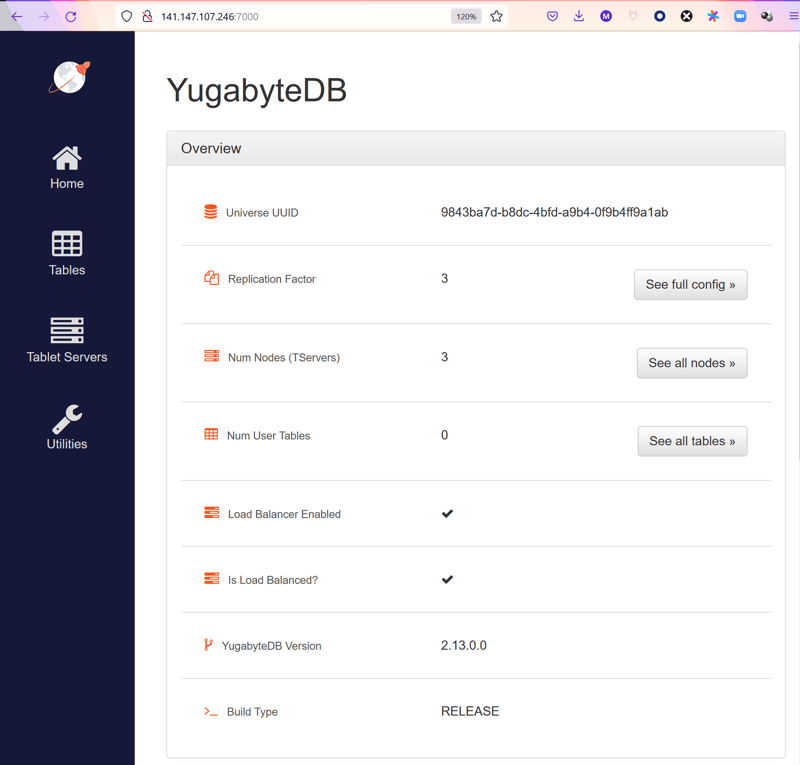
Port 7000 is the master web console, which I can access by its extenal IP, which I've put on the public network for this lab: http://141.147.107.246:7000
for the moment, the database is empty but in the next post I'll run some SQL. The PostgreSQL-compatible enpoint is exposed by the tserverload balancer: postgresql://141.147.106.110:5433/yugabyte:
$ psql postgresql://141.147.106.110:5433/yugabyte
psql (13.5, server 11.2-YB-2.13.0.0-b0)
Type "help" for help.
yugabyte=# select * from yb_servers();
host | port | num_connections | node_type | cloud | region | zone | public_ip
----------------------------------------------------+------+-----------------+-----------+--------+-------------+-------+----------------------------------------------------
yb-tserver-1.yb-tservers.yb-demo.svc.cluster.local | 5433 | 0 | primary | cloud1 | datacenter1 | rack1 | yb-tserver-1.yb-tservers.yb-demo.svc.cluster.local
yb-tserver-0.yb-tservers.yb-demo.svc.cluster.local | 5433 | 0 | primary | cloud1 | datacenter1 | rack1 | yb-tserver-0.yb-tservers.yb-demo.svc.cluster.local
yb-tserver-2.yb-tservers.yb-demo.svc.cluster.local | 5433 | 0 | primary | cloud1 | datacenter1 | rack1 | yb-tserver-2.yb-tservers.yb-demo.svc.cluster.local
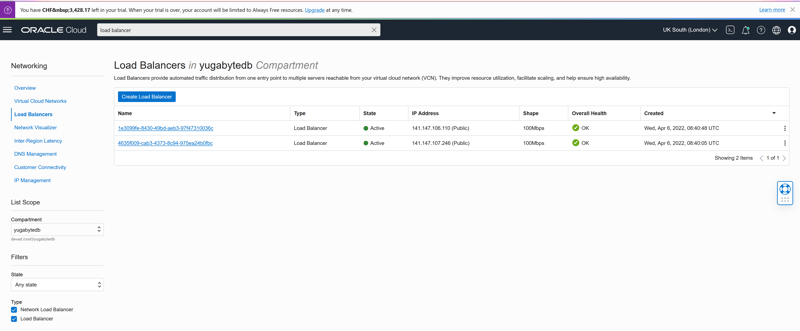
I have queried the yb_servers() function that returns the information about all nodes. Note that the public_ip here is the address within the Kubernetes cluster. From outside, we use the load balancers that have been automatically created by OKE, also tagged with OKEclusterName: yugabytedb:
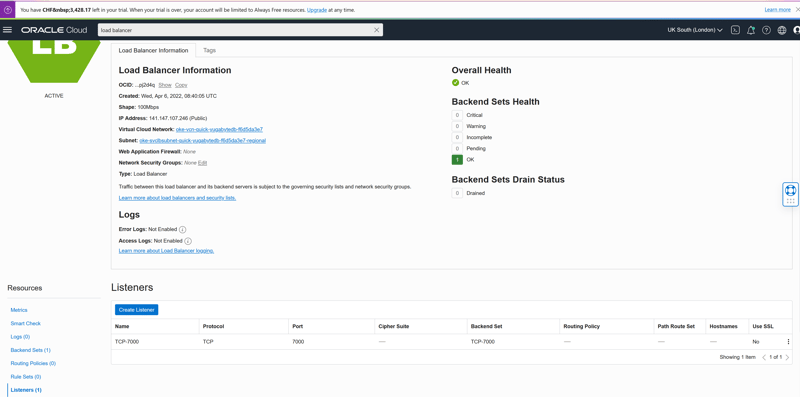
On is the master console, 141.147.107.246, listening on port 7000:
The other is the tserver service, 141.147.106.110, listening on:
- 5433 the YSQL endpoint (the PostgreSQL-compatible API)
- 9042 the YCQL endpoint (the Cassandra-compatible API)
- 6379 the YEDIS enspoint (the REDIS-compatible API)
Because YugabyteDB, in addition to be shared-nothing distributed SQL database, is also multi-API.
I'll use the PostgreSQL compatible API in the next post to generate some load. My goal is to use some storage and network transfer to evaluate the cost on the Oracle Cloud